Deploying Lambda Functions with SAM CLI
Serverless applications are a relatively new paradigm in software development. Serverless architectures allow developers to create, access and deploy applications without managing servers or infrastructure.
What is the AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM)?
AWS SAM is an open-source framework for building serverless applications. It provides shorthand syntax to express functions, APIs, databases, and event source mappings. You can define the application you want and model it using YAML with just a few lines per resource.
In this blog post, you will explore the Serverless Application Model framework, SAM template anatomy, and SAM CLI.
We’ll take a look at how you can create a new SAM app, and manually deploy it to AWS Cloud.
Prerequisites
- AWS SAM CLI is a command-line tool that operates on an AWS SAM template and application code. To install SAM CLI please follow the AWS official documentation.
- S3 Bucket to upload the packaged application artifact for deployment.
Code Repository
GitHub URL for the SAM application – https://github.com/avasisht/sam-app
Creating SAM application
To deploy the AWS SAM application using SAM CLI, you need
- SAM template file, SAM template closely follows the AWS CloudFormation template file format, the primary difference between the two is Transformation declaration.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: 'AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31'
Description: An Amazon Connect Lambda function.
Parameters:
Origin:
Description: Approved Origin for amazon connect instance
Type: String
Default: https://www.example.com
Identity:
Description: Amazon Connect Instance Identity Provider
Type: String
AllowedValues:
- CONNECT_MANAGED
- SAML
Default: CONNECT_MANAGED
InstanceName:
Description: Amazon connect Instance Name
Type: String
Default: connect-instance-name
Resources:
ConnectFunction:
Type: 'AWS::Serverless::Function'
Properties:
Handler: lambda.lambda_handler
Runtime: python3.9
CodeUri: srcin/
Description: An Amazon Connect Lambda function.
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 300
Environment:
Variables:
ConnectInstanceName: !Ref InstanceName
Identity: !Ref Identity
Origin: !Ref Origin
Policies:
- Statement:
- Sid: IAMPutRolePolicy
Effect: Allow
Action:
- iam:PutRolePolicy
Resource: '*'
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AmazonConnect_FullAccess
- Source code, of your lambda function. In this example, you are deploying a Python Lambda function to create an Amazon Connect Instance.
You can deploy any function of your choice, make sure you adjust the template file accordingly. For example, environment variables, IAM roles, policies, etc.
import uuid
import json
import time
import sys
import os
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
#generate a uuid
print(boto3.__version__)
uuId = str(uuid.uuid4())
uuidSplit = uuId.split("-")[4]
bucketName = os.environ['ConnectInstanceName'] + uuidSplit
instanceAlias = os.environ['ConnectInstanceName']
conClient = boto3.client('connect') #we will need to specify region on this
#create a connect instance
conResponse = conClient.create_instance(
ClientToken=uuId,
IdentityManagementType=os.environ['Identity'],
InstanceAlias=instanceAlias, #generates a random instance alias
InboundCallsEnabled=True,
OutboundCallsEnabled=True
)
#get the arn and ID, we will need those later
arn = conResponse['Arn']
connectId = conResponse['Id']
#Wait maybe? This would be better accomplished with a Step Function
time.sleep(90)
# Create S3 Bucket
s3Client = boto3.client('s3')
s3response = s3Client.create_bucket(
ACL='private',
Bucket=bucketName,
CreateBucketConfiguration={
'LocationConstraint': 'ap-southeast-2'
},
ObjectLockEnabledForBucket=False
)
# get the ARN of AWS issued KMS Key for Connect
kmsClient = boto3.client('kms')
kmsResponse = kmsClient.describe_key(
KeyId='alias/aws/connect'
)
print(kmsResponse)
kmsKeyId = kmsResponse['KeyMetadata']['Arn']
time.sleep(15)
# Associate Storage, these must be done one at a time
conStorageResponse = conClient.associate_instance_storage_config(
InstanceId=connectId,
ResourceType='CHAT_TRANSCRIPTS',
StorageConfig={
'StorageType': 'S3',
'S3Config': {
'BucketName': bucketName,
'BucketPrefix': 'ChatTranscripts',
'EncryptionConfig': {
'EncryptionType': 'KMS',
'KeyId': kmsKeyId
},
},
}
)
conStorageResponse = conClient.associate_instance_storage_config(
InstanceId=connectId,
ResourceType='CALL_RECORDINGS',
StorageConfig={
'StorageType': 'S3',
'S3Config': {
'BucketName': bucketName,
'BucketPrefix': 'CallRecordings',
'EncryptionConfig': {
'EncryptionType': 'KMS',
'KeyId': kmsKeyId
},
},
}
)
conStorageResponse = conClient.associate_instance_storage_config(
InstanceId=connectId,
ResourceType='SCHEDULED_REPORTS',
StorageConfig={
'AssociationId': 'string',
'StorageType': 'S3',
'S3Config': {
'BucketName': bucketName,
'BucketPrefix': 'Reports',
'EncryptionConfig': {
'EncryptionType': 'KMS',
'KeyId': kmsKeyId
},
},
}
)
conAddOrigin = conClient.associate_approved_origin(
InstanceId=connectId,
Origin= os.environ['Origin']
)
#we're done
return {
'connectArn': arn,
'bucketName': bucketName,
'instanceAlias': instanceAlias,
'status': 200
}
Now you have SAM files ready, let’s package and deploy the solution to AWS cloud using SAM CLI.
SAM Package and Deploy
To Package the AWS SAM application, run the sam package command. This command creates an output file, a .zip file of your code and dependencies, and uploads the file to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
sam package --s3-bucket "s3-bucket-name" --template-file "template-file" -name --output-template-file "output-file-name" --profile aws-profile
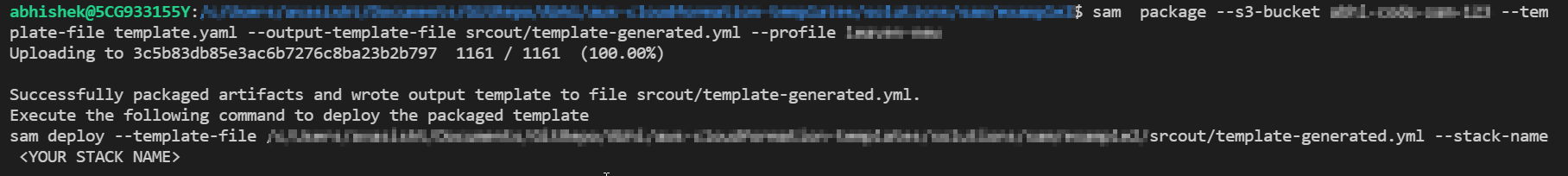
Our SAM application directory structure looks something like.
abhishek@5CG933155Y:$ tree
.
├── srcin
│ └── lambda.py
├── srcout
│ └── template-generated.yml
└── template.yaml
To Deploy the packaged AWS SAM application, run the sam deploy command.
sam deploy --template-file "srcout/template-generated.yml" --stack-name "cf-stack-name" --parameter-overrides "Key1=Value1 Key2=Value2" --capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM --profile aws-profile
In the deploy command, you have to refer to the output file “template-generated.yml” generated in the previous step.
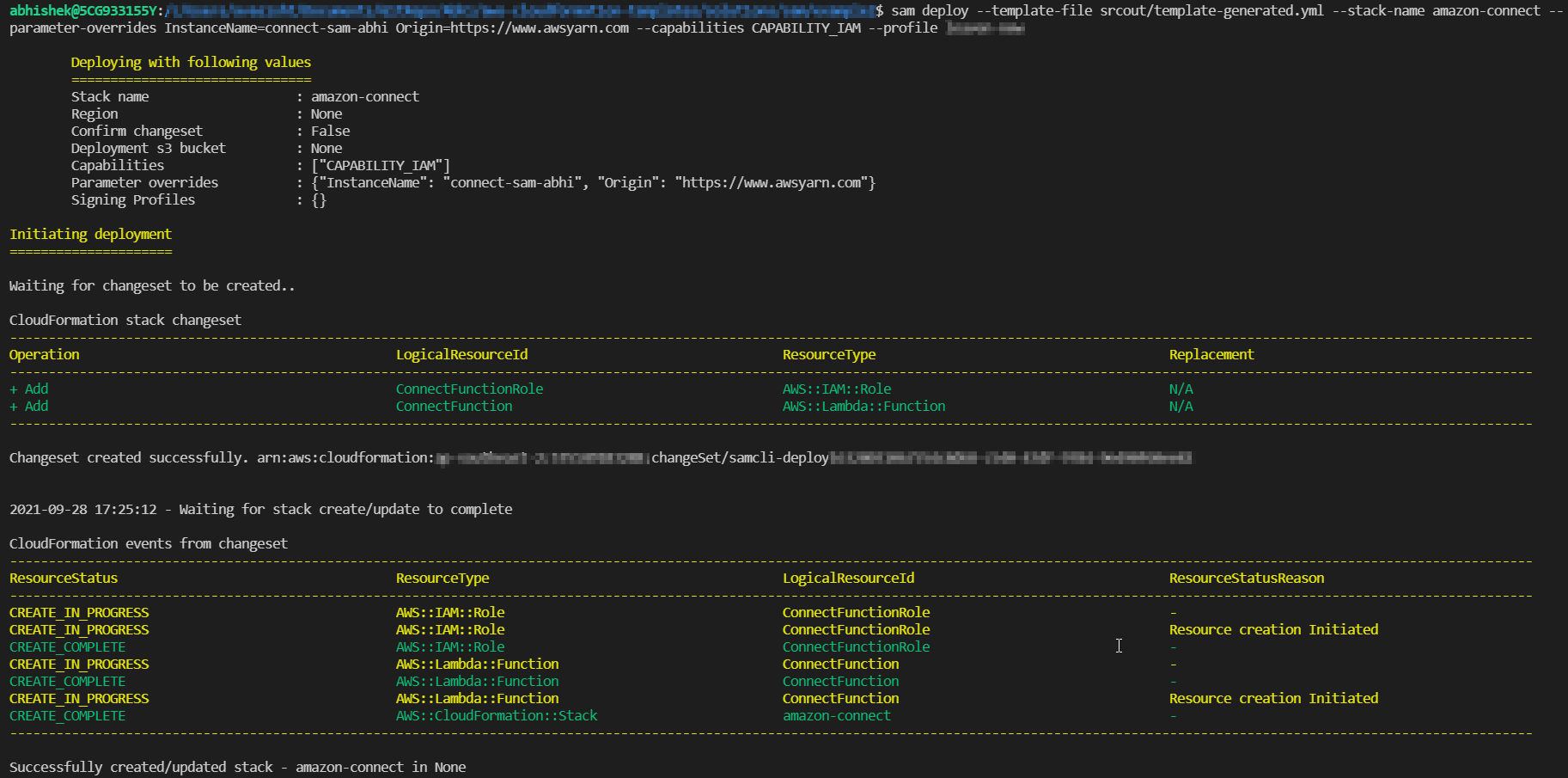
Woo-Hoo, you have successfully deployed a Lambda function using AWS SAM CLI.
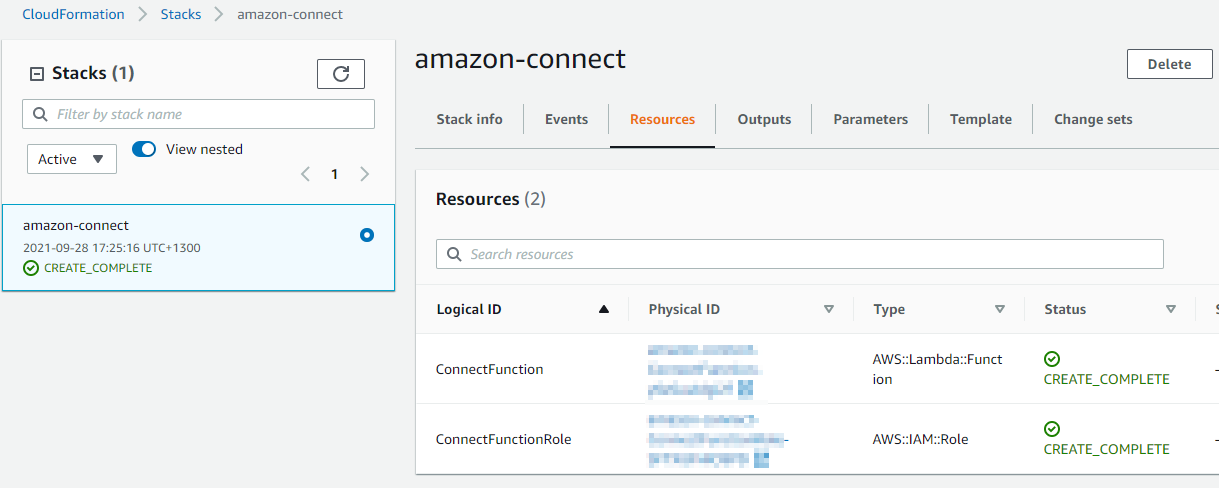
Validation
Log in to the management console and navigate to the CloudFormation Service and confirm the stack has been created successfully.
Clean Up
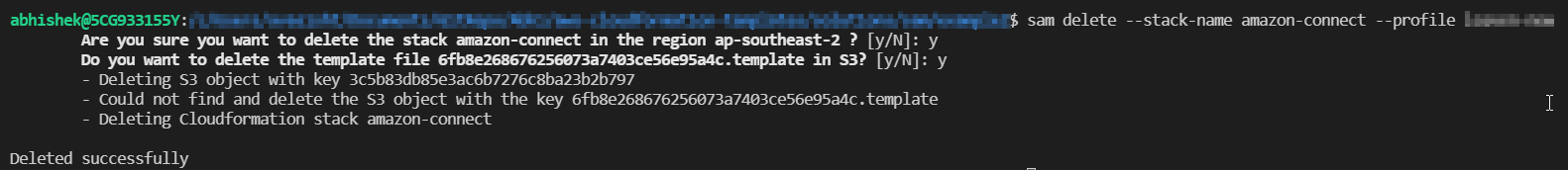
To clean up the resources created using SAM CLI, execute the sam delete command.
sam delete --stack-name "stack-name" --profile "aws-profile"
Conclusion
The AWS SAM framework is a new way to manage the serverless application life cycle. With SAM CLI, developers can quickly build, package, and deploy serverless applications, which includes services like lambda functions, API gateways, DynamoDb tables, Cloudwatch event rules, etc.. in a few steps. Using this model has many benefits, such as a single deployment configuration not requiring additional resources or skillset knowledge. It also has built-in best practices, saving time setting up IAM roles, policies, enforcing code reviews, and more. It helps developers focus on what they do best – developing solutions! with little code.
